Java LinkedHashMap Internal Implementation
LinkedHashMap is the data structure used to store the key-value pairs like HashMap but it guarantees the order of insertion(unlike the HashMap). So the elements are stored in the order of their insertion.
Please go through the internal working oh HashMap at https://goo.gl/tMVF3g before diving into the LinkedHashMap.
Brief about HashMaps:
a. HashMap stores key-value pairs in Nodes.
b. put() method returns the old value of the Node if the Node to insert also already exists in the HashMap before.
c. put() method returns null if the Node with the same key was not present before in the HashMap, and this Node is inserted for the first time.
d. get() method returns null if the Node is not present in it.
e. get() method returns the value of the Node if Node is present in the HashMap.
Now while iterating over the Hashmap starting from the 0th index to the nth index of the array table, and at every index iterating over the linked list at that index. Hence the order of insertion is not maintained here.
To maintain the order of insertion we need 2 more pointers at every Node(besides the next pointer required for LinkedList functionality). So besides this linkedList, another doubly-linked-list is also maintained in the hashmap which is used to handle the insertion order.
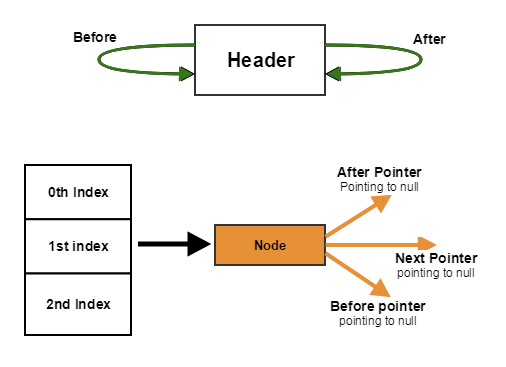
So the LinkedHashMap Node(named LinkedHashMapEntry) will look like:
i.e. a total of 6 fields now.
before: points to the node inserted before this node
after: points to the node inserted after this node
key: key as provided
value: value as provided
next: points to the next node in the same bucket of array table(like in HashMap)
hash: hashcode to calculate the index of this node, and check for equality.
Also, there is the header field in the LinkedHashMap:
which points to the head of our doublyLinkedList.
In the initialization phase, the header is set with null values and -1 hash as it is of no use to us, but just a marker node to represent the head of the List.
The after and before all points to itself initially as:
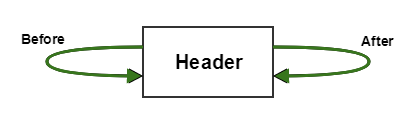
So that is the beginning of our doubly linked list.
Note: Header has null key and value and -1 hashcode. But we need not worry about its null key as it is not inserted into hashmap. Hashmap maintains other LinkedList for elements to insert into it, and its not a part of it. But instead its the header for our other linkedlist used for insertion purpose
put() operation:
The basic put operation will work in the same way as in HashMap. Please refer to https://goo.gl/tMVF3g put() operation, which adds the element in the correct bucket index and at the top of the LinkedList present there.
Noe the next pointer points to the next element at that bucket index to the next element at the same bucket index.
But still, the order is not maintained, as our before and after are not set for this node.
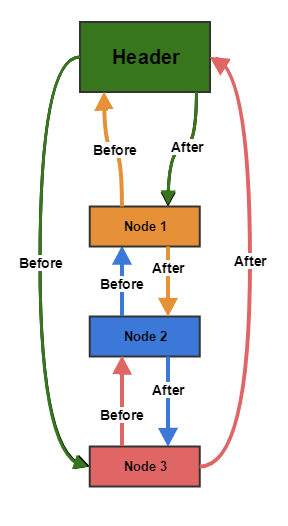
So let after insertion our the state of the LinkedHashMap is:
i.e. Node 1 inserted at index 1. As its end of LinkedList of hashMap, its next points to null which is OK.
But it is before and after are also pointing to null. So we need to link this node to the second LinkedList i.e. with the header field.
So to link the newly added element with the header, it is added before the header as:
Here the header is passed as the existing entry parameter.
So
Line1: “after” of newly inserted Node now points to the header(to complete the circular list)
Line 2: “before” of newly inserted Node now points to the previously inserted entry i.e. header’s-before value(header’s-before always points the last inserted Node), i.e. it's before now points to the second last inserted Node(as it becomes the last node now).
It will be more clear with the below images.
Line 3: Second last entry’s after points to this newly inserted Node.
Line 4: header’s before points to this newly inserted Node.
Let us make it clearer with the Images.
Initially, the LinkedHashMap looks like this:
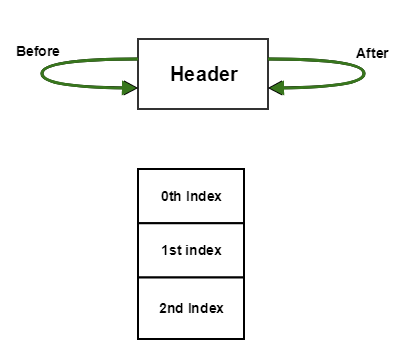
now Put 1 into it.
The LinkedHashMap now becomes:
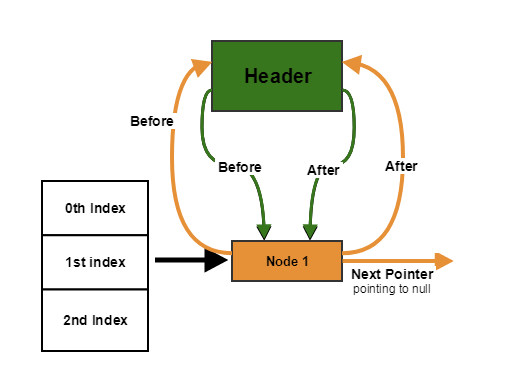
So after Node1 is inserted by regular hashMap put() code, running the above code i.e. :
generates
Line 1: Node1.after = header
Line 2: Node1.before = (header.before) and header.before = header
so Node1.before = header
Line 3: Node1.before.after i.e. header.after = Node1
Line 4: Node1.after.before i.e. header.before= Node1
As illustrated in the image above.
So state till now:
Header.before = Node1
Header.after = Node1Node1.before = header
Node1.after = header
so we have header -> Node1 -> header
Now put another element say Node 2 and the state will then become:
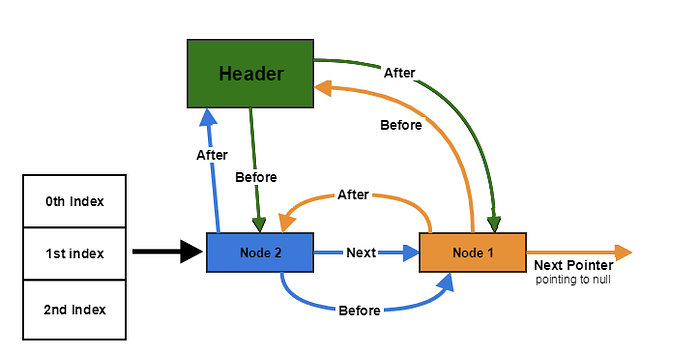
Let the Node2 also is added at index 1. So as per put() of hashmap, it inserts the Node2 before Node1 with its next pointing to Node1 as shown.
Running the above algo again:
Line 1: Node2.after = header
Line 2: Node2.before = (header.before) and header.before = Node1
so Node2.before = Node1
Line 3: Node2.before.after i.e. Node1.after = Node2
Line 4: Node2.after.before i.e. header.before= Node2
So state till now:
Header.before = Node2
Header.after = Node1(unchanged)Node1.before = header(unchanged)
Node1.after = Node2Node2.before = Node1
Node2.after = header
i.e. header -> Node1 -> Node2 [Considering the after]
Lets try putting one more element after this.
Let's put Node3 which is placed at index 2 say.
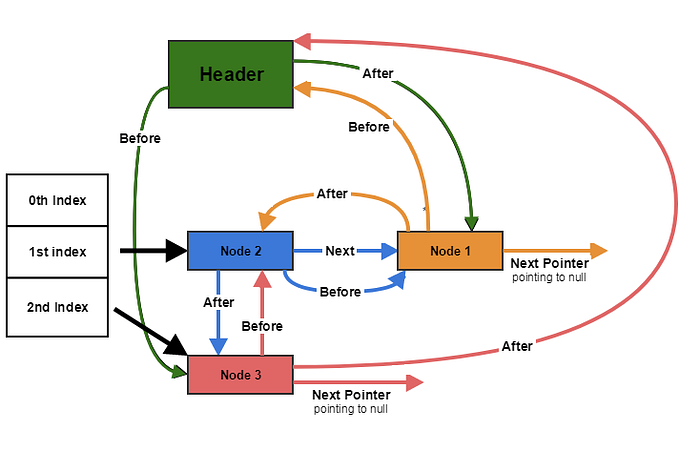
Running the algo again on previous state
Node2.before = Node1
Node2.after = header
Node1.before = header
Node1.after = Node2
Header.before = Node2
Header.after = Node1
Line 1: Node3.after = header
Line 2: Node3.before = (header.before) and header.before = Node2
so Node3.before = Node2
Line 3: Node3.before.after i.e. Node2.after = Node3
Line 4: Node3.after.before i.e. header.before= Node3
So the state becomes:
Header.before = Node3
Header.after = Node1(unchanged)Node1.before = header(unchanged)
Node1.after = Node2(unchanged)Node2.before = Node1(unchanged)
Node2.after = Node3Node3.before = Node2
Node3.after = header
So as seen we have 2 different types of linked lists:

The one that is created with hashMaps.
And the other LinkedList created for insertion maintenance.